Private Children’s Hearing Test
Hearing is a crucial sense that enables us to communicate, learn, and navigate the world around us. Children with hearing loss can face significant developmental delays, so early detection and intervention are essential. At Verified Hearing we provide private hearing tests for children in our state-of-the-art hearing clinic in London. Children attend our clinic from all over the UK and abroad.
Remember, your child may not be ignoring you; they probably just can’t hear you
Special Offers
- Free online consultation: You can speak to one of our Paediatric Audiologists over the phone about the concerns you have regarding your child’s hearing.
Book Here - Weekend appointments: You don’t need to take time off work and your little one does not have to miss school. We have created two additional slots for Saturdays and Sundays.
- Sibling free ear check and discount: If your child has a sibling, we can check their ears for free on the day. If the sibling needs a hearing test they get 50% off.
- Blue light discount: If you work for the emergency services, NHS, social care sector and armed forces you get 20% off call 0203 011 1280 to book
Accredited practitioners



OR
Book a FREE online consultation
- Worried about your child’s hearing or speech but not sure how to navigate or if they need a hearing test?
- Speak to one of our friendly Paediatric Audiologist for
FREE
Consultations take only on 10mins
What our patients say
Why parents book our private children’s hearing test

Prompt service delivery
Pressure on the NHS has meant significantly longer waiting times for crucial services like paediatric audiology. Hearing is essential to your child’s speech and language development. Understandably, parents want to know their child’s hearing status as quickly as possible. At Verified Hearing, we would typically see your child for a hearing test within 24-72 hours of initial contact.

Comprehensive ear care
Comprehensive service including children ear wax removal. The last thing you want to hear after waiting so long for your child’s hearing test is “sorry they have ear wax so we can’t do the hearing test. Use olive oil and return in 3 months”. We do not do that. If your child has ear wax, we remove the wax on the day of the appointment and proceed with the hearing test.

Specialist Paediatric Audiologists
We employ some of the most talented private paediatric audiologists in the UK who just love working with children.

Signs of hearing loss in children
Your child may have a hearing loss if they are displaying any of these symptoms:
- Speech delay: The most common red flag for hearing loss in toddlers is speech delay. Children cannot reproduce sounds they can’t hear. We find children with hearing loss mispronounce or substitute phonemes/words sometimes.
- Child not responding to their name: Babies recognise their name consistently around 7-9 months old. If your toddler does not respond to their name, they may be experiencing hearing loss.
- Behavioural concerns: Your child may display unusual behaviour which parents and teachers may interpret as “not listening” or “ignoring”. It may simply be that your child cannot hear and is frustrated because they are unable to express themselves.
- Speaking loudly: It is difficult for your child to regulate the volume of their voice if they can’t hear themselves.
- Having the TV or Ipad Volume louder than other prefer it
- Asking for constant repetitions: A few “pardons” are fine but if you or your child’s teacher thinks they are asking for more repetitions than usual, your child may be experiencing a hearing loss.
- Learning difficulty: Hearing loss can have an impact on your child’s learning. It is always a good idea to check their hearing if you or their teachers are concerned.
- Excessive tiredness: A hearing loss can cause increased listening effort which can make your child more fatigued than usual at the end of a normal day.
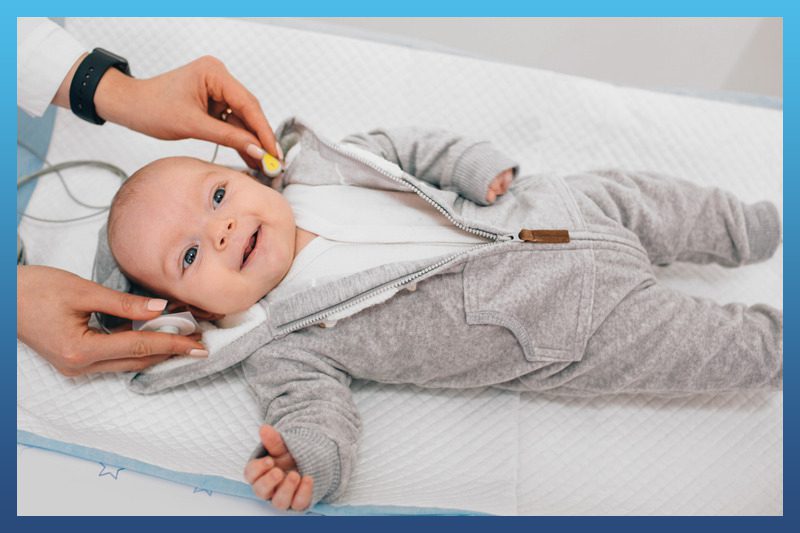
Hearing test for kids
Depending on your child’s age, we would perform a different kind of hearing test. We would typically see children who are 2.5 years and older.
Below is a description of the test we would perform based on your child’s developmental age:
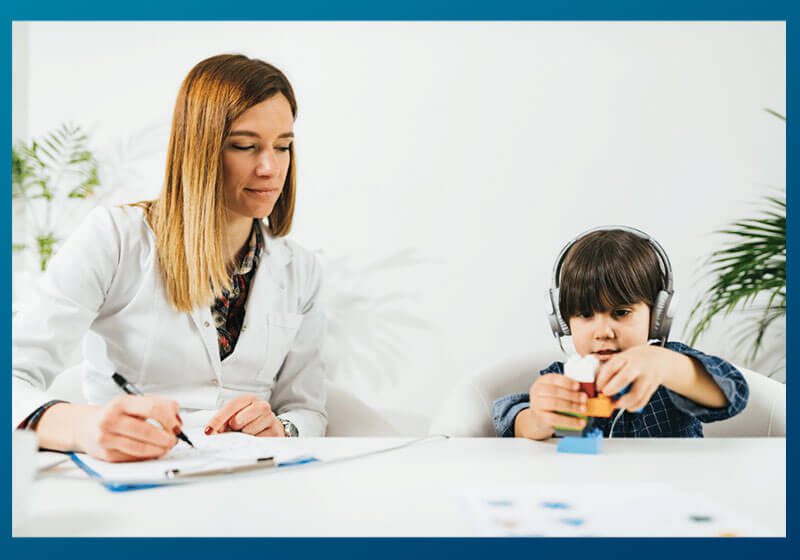
Play audiometry
Play audiometry aka the toddler hearing test is a hearing test that’s typically used for children 2.5 years and older. It’s a fun and interactive way to test a child’s hearing ability, using toys and other objects to encourage them to respond to sounds they hear.
During the test, the child wears headphones and sits on their caregiver’s lap. Our paediatric audiologist will play sounds at different frequencies and volumes through the headphones. When the child hears a sound, they’re encouraged to respond in some way, such as placing a toy in a bucket or pressing a button. The audiologist will then record the child’s responses and use them to assess their hearing ability.
Play audiometry can take anywhere from 10 to 30 minutes, depending on your child’s developmental age and attention span. It’s a non-invasive and painless test, and most children find it to be enjoyable and engaging.
Puretone Audiometry
Speech audiometry measures your child’s ability to hear and understand speech. This test involves playing recorded speech at different volumes and asking the child to repeat back what they hear. For younger children we may focus on assessing their speech perception by presenting them with a number of familiar objects, then calling out one object e.g., “show me the plate” and record their reaction to this. Some children with hearing loss may show the “plane” instead of “plate” for instance.
Tympanometry
Tympanometry is a test that measures the movement of the eardrum relative to sound and gives us information on the state of the middle ear. It is a useful test for diagnosing common conditions such as glue ear which is most common in children under the age of 7. Except contraindicated, we perform tympanometry on all children as part of our comprehensive children’s hearing test.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)
OAEs is an objective test that is used to test the state of the outer hair cells. Healthy outer hair cells are a good indication of normal or near-normal hearing. This is why the hearing test in newborns is performed using OAE testing. When indicated, we will recommend your child has an OAE test to give us additional information on the state of your child’s inner ears.
What happens at your kid’s hearing test
We advise you to book a time slot where your child is most likely going to be alert.
- The Paediatric Audiologist asks you questions regarding your concerns about your child’s hearing. We encourage parents to bring their red book to the appointment.
- We examine your child’s outer ears. This process is called otoscopy.
- Your child is shown how to perform the hearing test (we call it the listening game for toddlers).
- After enough practice, once we are sure they understand the instruction, we proceed with the hearing test (this process is called conditioning).
- We continue engaging with the child and changing the game where needed to keep their attention.
- We perform a pressure test to check for glue ear or any other middle ear conditions.
- The results are discussed with you and we decide on the best management plan for your child.
- A report is sent out within 5 working days to the Parent(s)/Guardian(s) and other relevant professionals e.g. the Speech and Language Therapist (if we have your consent).
Causes of hearing loss in Children
Congenital Causes
Congenital causes of hearing loss refer to conditions that a child is born with. The most common congenital cause of hearing loss is genetic factors, which can cause both syndromic and non-syndromic hearing loss. Syndromic hearing loss in children is hearing loss associated with a specific medical condition or syndrome, such as Down syndrome or Usher syndrome. Children with syndromic hearing loss may have additional symptoms and medical problems beyond just the hearing loss, while non-syndromic hearing loss is not associated with any other medical condition. Other congenital causes of hearing loss include maternal infections during pregnancy, such as cytomegalovirus (CMV), rubella, and toxoplasmosis, which can cause sensorineural hearing loss. Premature birth and low birth weight are also associated with hearing loss.


Acquired Causes
Acquired causes of hearing loss refer to conditions that develop after birth. The most common acquired cause of hearing loss in children is otitis media, an infection of the middle ear that can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss. Other infections that can cause hearing loss include meningitis and measles. Exposure to loud noise, such as loud music or industrial noise, can also cause hearing loss in children. Head injury, certain medications, and certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, can also cause hearing loss.
Conductive vs. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hearing loss in children can be classified as conductive or sensorineural. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is not conducted efficiently through the outer ear, middle ear, or both. This type of hearing loss can be caused by conditions such as otitis media, congenital malformations of the ear, or earwax buildup. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. This type of hearing loss can be caused by genetic factors, infections, head trauma, and exposure to loud noise. If your child has a hearing loss, we will be able to advise what kind of hearing loss and offer the relevant advice.
Meet our team
Head of Audiology at Verified Hearing (Specialising in adults and children)
Secretarial team

Louise Emmett

Paige Martin

Leah Salter

Rebecca Banks

Ayesha Haworth
Frequently Asked Questions
What people are asking
References:
- Nance WE, Lim BG, Dodson KM. Importance of congenital cytomegalovirus infections as a cause for pre-lingual hearing loss. Feb, 2006 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1386653205003057 . [online] Available at: [Accessed September 13, 2023].
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021. Genetics of Hearing Loss | CDC. [online] Available at: [Accessed 17 September 2023].


















